43 two genes of a flower
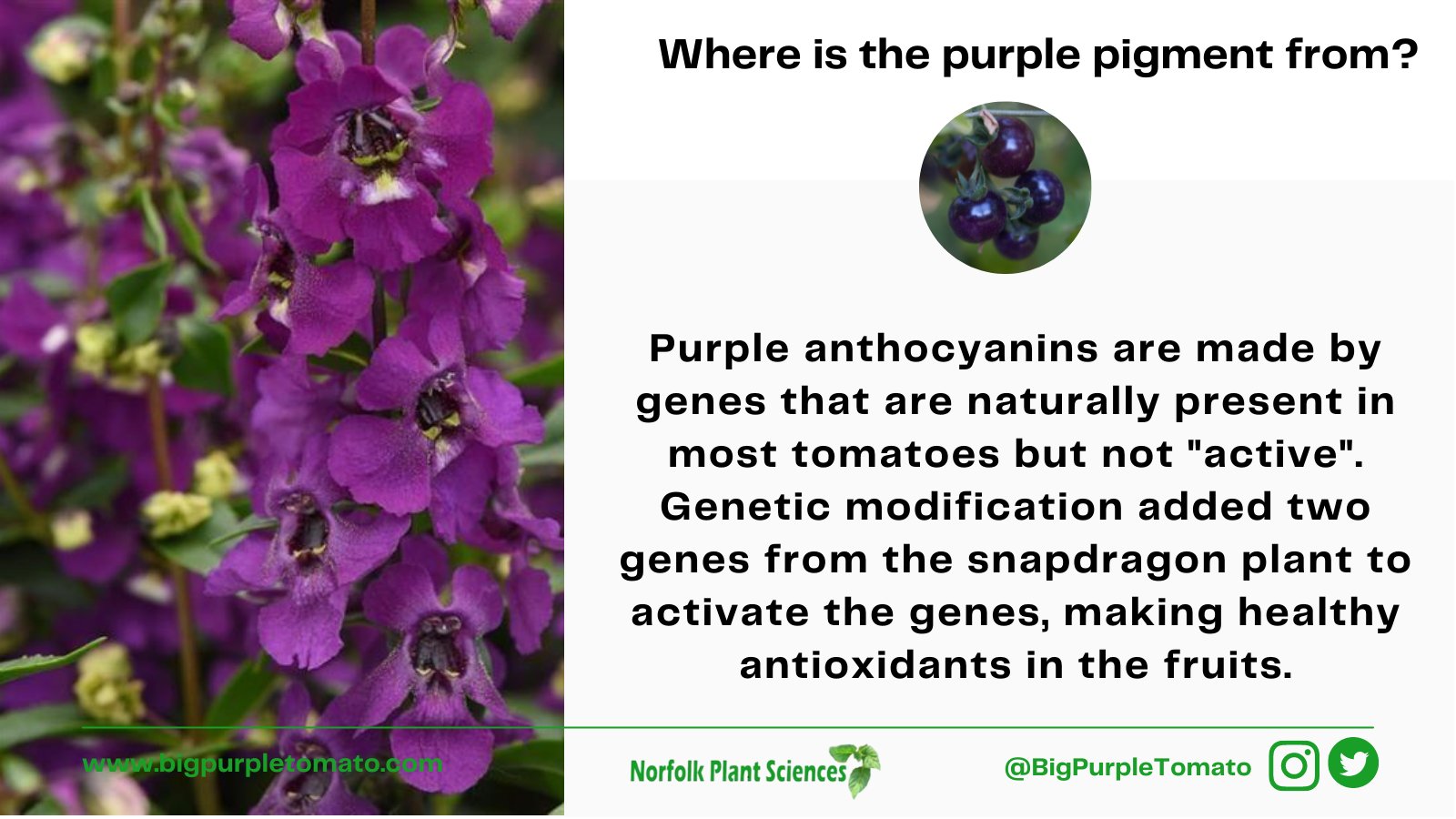
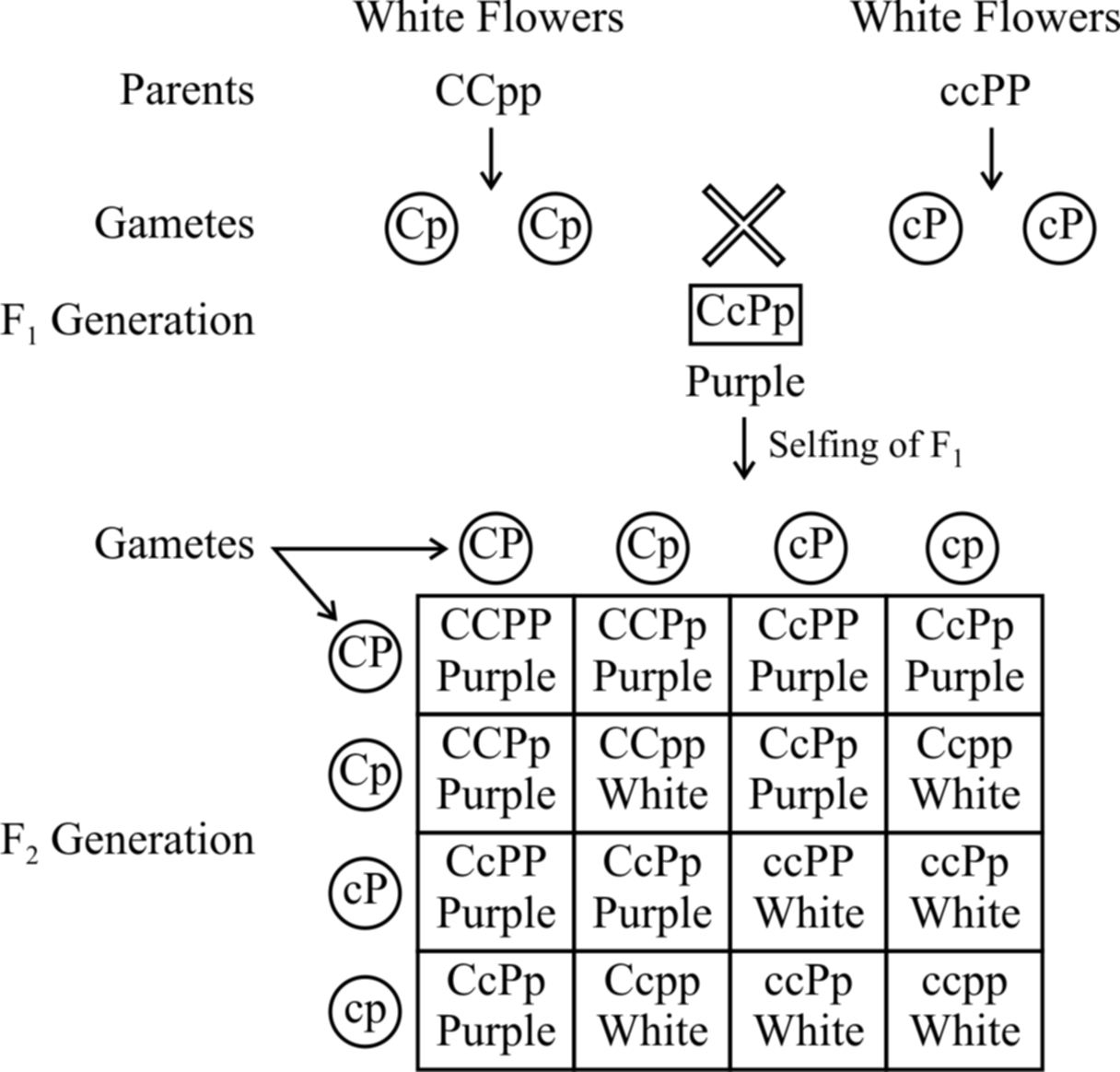
Genes responsible for difference in flower color of snapdragons ... In the snapdragons, these islands correspond to genes responsible for flower color. The recent paper focuses on two of those genes, which determine the magenta pigment, and are located close ... Genetics Test #1 Flashcards | Quizlet White flowers (Enzyme A) ——-> White flowers (Enzyme B) ——-> Purple flowers (Question 6) Two white-flowered true-breeding plants with genotypes AAbb and aaBB are crossed. All of the F1 are AABb and have purple flowers. Select the molecular pathway that will result in purple flowers in the F1. an environmentally-influenced trait
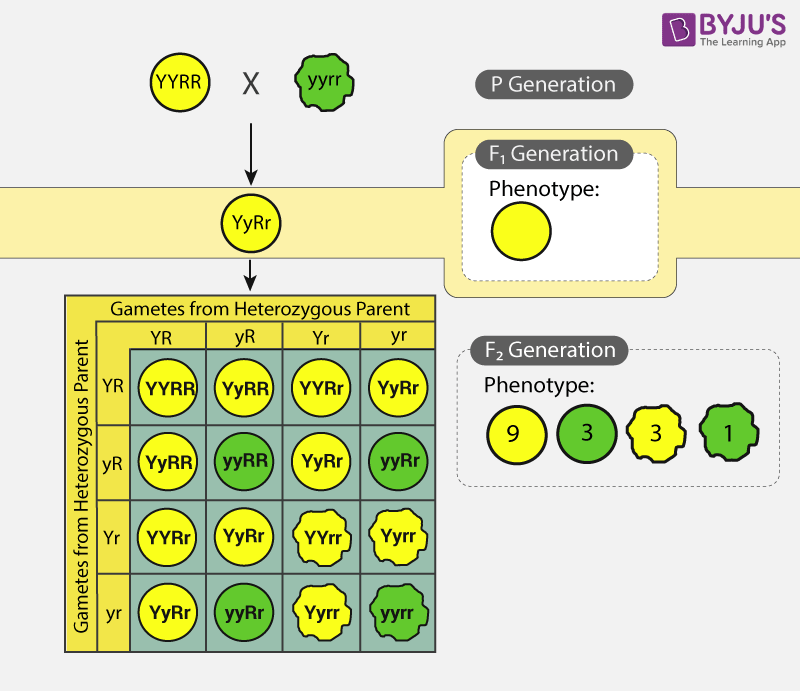
Inheritance of Two Genes: Meaning, Example, and Importance - Embibe Exams Inheritance of Two Genes Examples Dihybrid Cross in Pea plants The cross between a homozygous pea plant with round yellow seeds and green wrinkled seeds is an example of a dihybrid cross. As discussed earlier, RY, Ry, rY, and ry are four possible combinations of the four alleles.
Two genes of a flower
Two Genes Crucial for Plants Colonizing the Earth 470 ... - SciTechDaily They specifically demonstrated that two genes are crucial for terrestrial plants to protect themselves against fungal attack - a defense mechanism that dates back 470 million years. These defenses most likely paved the way for all terrestrial plant life. Mads Eggert Nielsen, a University of Copenhagen biologist. Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue ( $B$ ) versus white - Numerade Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue ( B ) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round ( R ) versus oval ( r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue-oval plant with a homozygous white-round plant. Answered: Two genes of a flower, one controlling… | bartleby Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round (R) versus oval (r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue oval plant with a homozygous white round plant. The resulting F1 progeny are crossed with homozygous
Two genes of a flower. Flower Meristem Identity - University of California, San Diego Meristem Identity Genes can be divided into two distinct classes.. The first class promotes flower meristem identity, and includes LEAFY, APETALA1 and CAULIFLOWER together with UNUSUAL FLORAL ORGANS (UFO), and others.; The second class has the opposite effect, and maintains the identity of inflorescence shoot meristems, and includes TERMINAL FLOWER. Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) versus white ... Jan 06, 2019 · answered. Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round (R) versus oval (r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue oval plant with a homozygous white round plant. The resulting F1 progeny are crossed with homozygous white oval plants, and 1,000 offspring plants are obtained. Genes Types: Top 6 Types of Genes | Genetics - Biology Discussion The cross between the two white varieties can be explained by assuming two genes for red colour which must be present together, i.e., must act in a complementary way to each other. ... If one of the two genes for red colour is absent, the result is a white flower. This explanation can be verified by making a checkerboard. Biology Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet d. knowledge of the location of the alleles for flower color d. knowledge of the location of the alleles for flower color In Mendel's controlled mating experiments, the individuals produced by crossing two true-breeding parents are referred to as a. the P generation. b. the F1 generation. c. the F2 generation. d. dihybrids. b. the F1 generation.
Gene Interactions - North Dakota State University The interactions of the two genes which control comb type was revealed because we could identify and recognize the 9:3:3:1. Other genetic interactions were identified because the results of crossing two dihybrids produced a modified Mendelian ratio. ... Example: Flower color in sweet pea If two genes are involved in a specific pathway and ... Test Cross (Single, Two, Triple Gene)- Definition, Examples, Uses Hence, the test concludes that the test flower was heterozygous red (Rr). B. Dihybrid Test Cross (Two Gene Test Cross) Also called 'two-gene test cross', is a type of testcross where two types of genes or phenotypic characters are studied. Among different characters of test individuals, only two of the dominant characters are considered. In a species of plant, two genes control flower color. In a species of plant, two genes control flower color. The red allele (R) is dominant to the white allele (r); the color-producing allele (C) is dominant to the non-color-producing allele (c). You suspect that either an rr homozygote or a cc homozygote will produce white flowers. In other words, rr is epistatic to C, and cc is epistatic to R. Examples of Gene Flow in Plants and Animals - YourDictionary Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area. Any time a gene is introduced into a population where that gene once did not exist, gene flow has occurred. Discover some gene flow examples in both the plant and animal kingdoms.
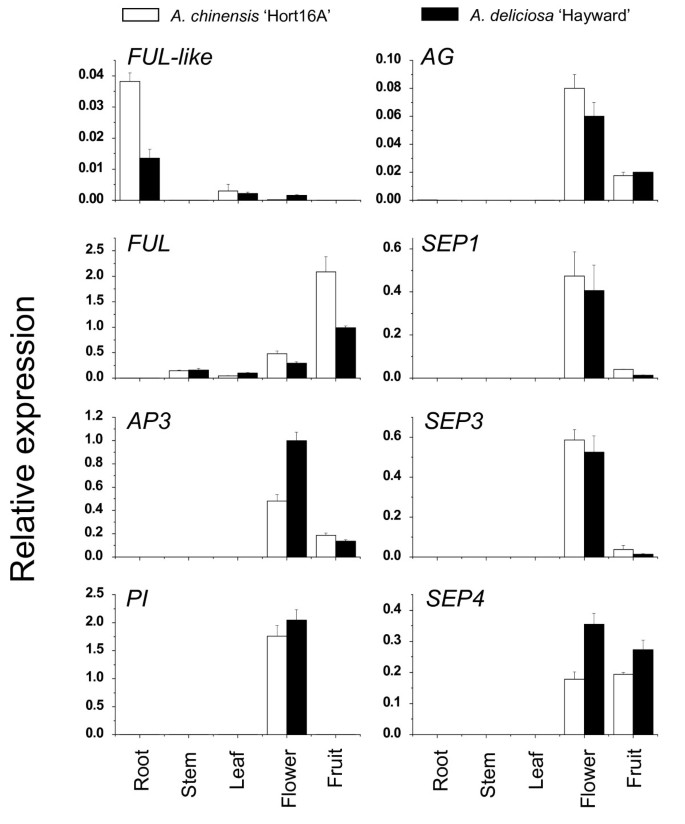
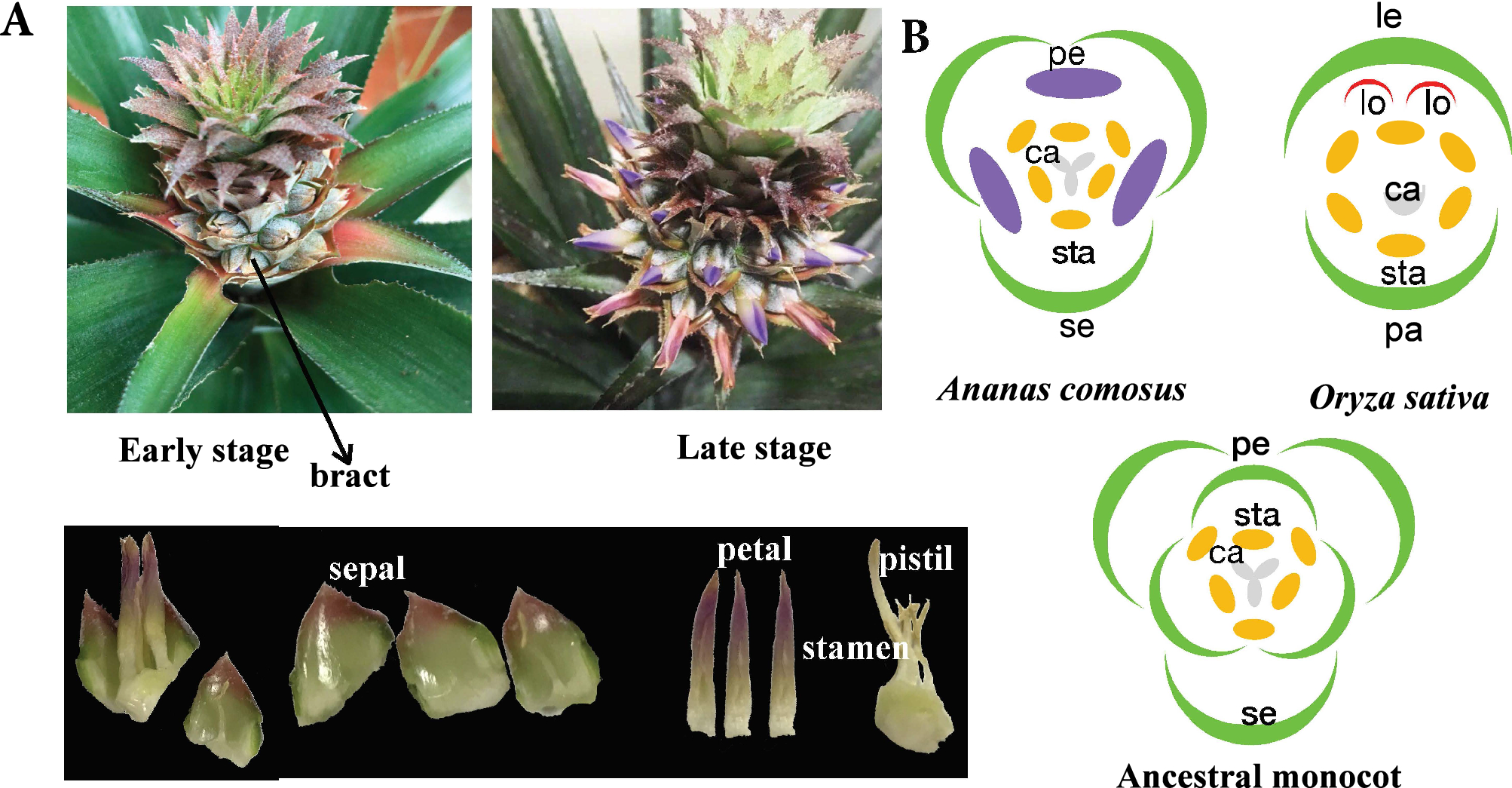
Genes Controlling Flower Development in Plants - Floral Organ Identity ... The two A function genes are APETALA2 and APETALA1. Alleles of these two genes have been isolated that show varying degrees of effect, but in general if an A function gene is mutated, the first whorl develops as a carpelc and the second whorl develops as a stamen. ovulata is an A function gene of snapdragon similar to APETALA2. What is a plant that has two dominant gene or two recessive genes ... Pure traits may have two dominant genes or two recessive genes. For example, a pea plant may have two genes for tallness, which is dominant trait in pea plants. This plant is homozygous plant with ... ABC model of flower development - Wikipedia The following three genes in Arabidopsis thaliana possess both common and independent functions in floral transition: FLOWERING LOCUS T ( FT ), LEAFY ( LFY ), SUPPRESSOR OF OVEREXPRESSION OF CONSTANS1 ( SOC1, also called AGAMOUS-LIKE20 ). [5] SOC1 is a MADS-box -type gene, which integrates responses to photoperiod, vernalization and gibberellins. Evidences for a role of two Y-specific genes in sex ... - Nature Two genes are present only in the Y-linked region. One is a duplication of a non-Y-linked, female-specifically expressed response regulator, which produces siRNAs that block this gene's expression,...
Solved QUESTION 57 Questions 57-60. Two genes of a flower, - Chegg Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round (R) versus oval () stamens, are linked and are 20 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue-round plant with a homozygous white-oval plant. The resulting F1 progeny are crossed with homozygous white-oval plants, and 1,000 F2
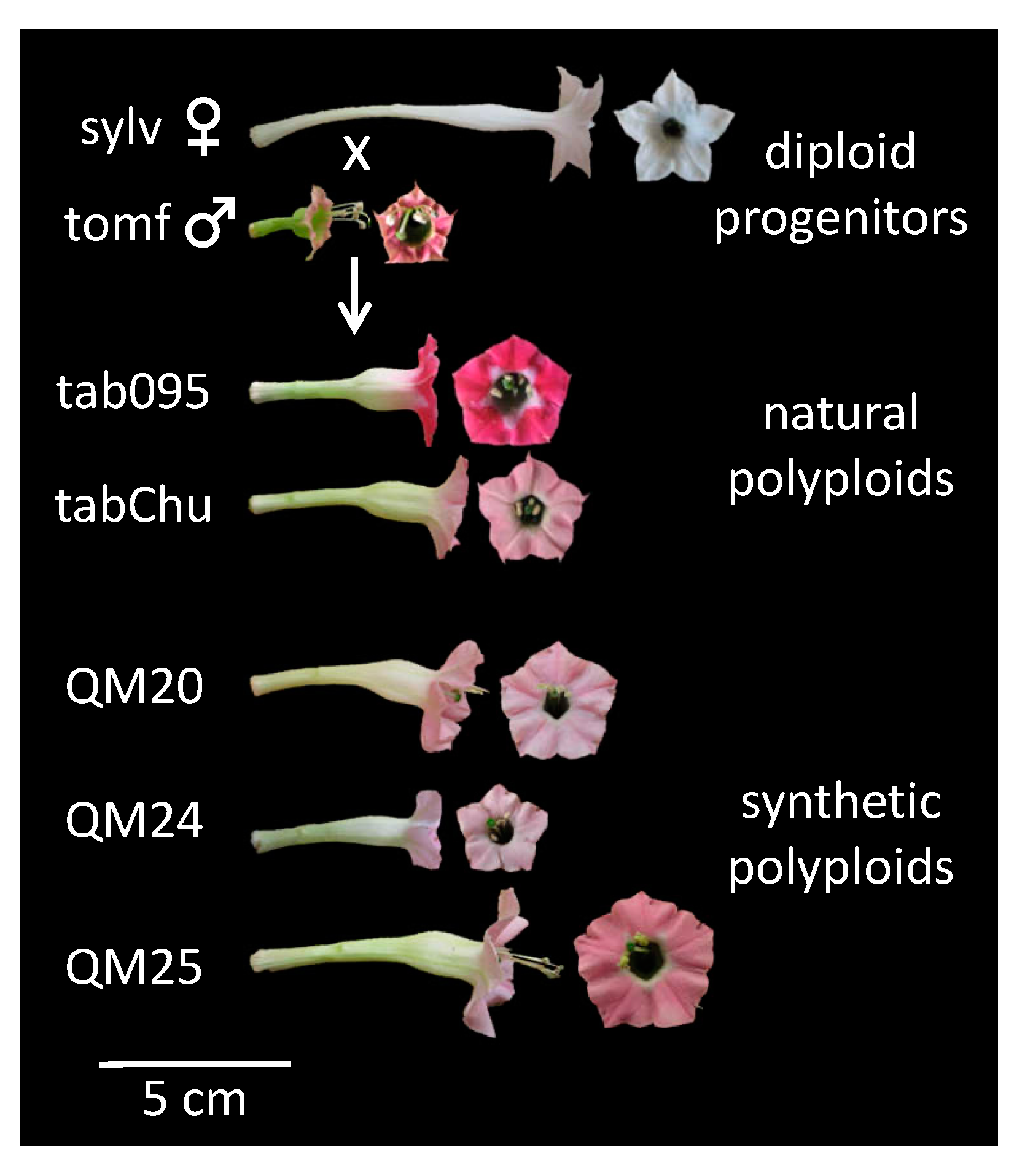
Plant genetics - Wikipedia Genetically modifying plants is an important economic activity: in 2017, 89% of corn, 94% of soybeans, and 91% of cotton produced in the US were from genetically modified strains. [21] Since the introduction of GM crops, yields have increased by 22%, and profits have increased to farmers, especially in the developing world, by 68%.
Transgenic Plant - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics Transgenic plants expressing (at 0.05-0.1% w/w of the total soluble protein) an insecticidal toxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) have been shown to be protected selectively against herbivorous larvae of lepidopteran, coleopteran, or dipteran pests. The main crops transgenic with Bt are corn, cotton, canola, potato, and tomato.
ABC Model of Flower Development | Plants - Biology Discussion (2) The observation that each of the genes that induce the formation of an organ in a flower has an effect on two groups of floral organs, i.e. sepal and petals or petals and stamens. Class A, B and C genes are homeotic genes. They determine the identity of different floral organs and induce the organs to develop in their respective whorls.
Solved Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) - Chegg Science Biology Biology questions and answers Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round (R) versus oval (r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue oval plant with a homozygous white round plant.
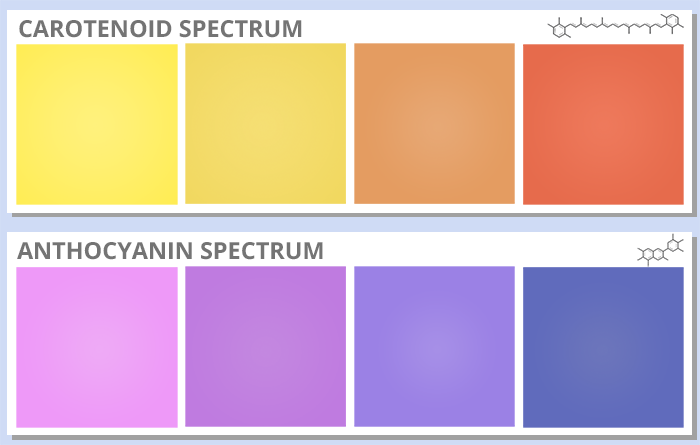
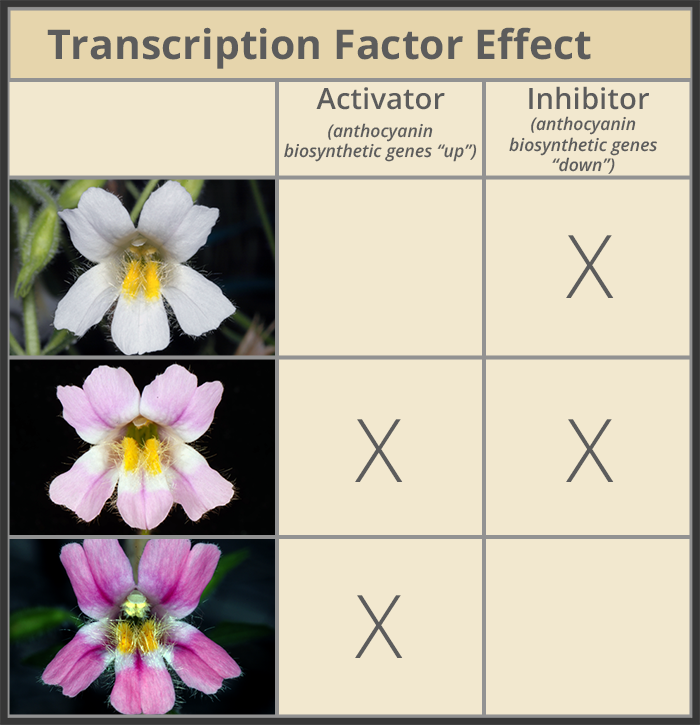
Carnation I locus contains two chalcone isomerase genes ... - PubMed Carnations carrying a recessive I gene show accumulation of the yellow pigment chalcononaringenin 2'-glucoside (Ch2'G) in their flowers, whereas those with a dominant I gene do accumulation the red pigment, anthocyanin. Although this metabolic alternative at the I gene could explain yellow and red flower phenotypes, it does not explain the development of orange flower phenotypes which result ...
Methods of Gene Transfer in Plants - Federation of American Scientists Two methods are used to transfer foreign genes into plants. The first method involves the use of a plant pathogen called Agrobacterium tumefaciens, which causes crown gall disease in many species. This bacterium has a plasmid, or loop of non-chromosomal DNA, that contains tumor-inducing genes (T-DNA), along with additional genes that help the T ...
The Genetics of Flower Color - University of Utah Two main groups of genes control flower color. One group includes genes that code for the protein machinery required to make pigment molecules. The other group includes genes that code for regulatory proteins. It's the regulatory proteins that control the location, type, and amount of pigment-producing machinery made. The Rainbow Road
Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (b) versus white (b) petals ... Dec 25, 2017 · Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (b) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round (r) versus oval (r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. you cross a homozygous blue-oval plant with a homozygous white-round plant. the resulting f1 progeny are crossed with homozygous white-oval plants, and 1,000 f2 progeny are obtained. how many f2 plants of each of the four phenotypes do you expect? _____ blue-oval : _____ white-round : _____ blue-round : _____ white-oval.
[Identification of Two GLOBOSA-like MADS-box Genes in Tea Plant ... In the present study, two GLOBOSA (GLO) -like MADS-box genes, CsGLO1 and CsGLO2, were isolated from C. sinensis 'Ziyangzhong' and were characterized to elucidate their roles in flower development. We found that CsGLOl and CsGLO2 are nuclear-localized transcription factors without transactivation ability but with a robust interaction.
PDF 5. GENE INTERACTIONS - Centurion University 7) Polymeric gene action (9:6:1): When two genes govern any character separately, their effect is equal but when both the genes are present together, there phenotypic effect is increased or raised as if the effects of the two genes were additive or cummulative. It is notable in this case that both the genes show complete dominance.
Answered: Two genes of a flower, one controlling… | bartleby Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue (B) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round (R) versus oval (r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue oval plant with a homozygous white round plant. The resulting F1 progeny are crossed with homozygous

two genes of a flower one controlling blue b versus white b petals and the other controlling round r
Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue ( $B$ ) versus white - Numerade Two genes of a flower, one controlling blue ( B ) versus white (b) petals and the other controlling round ( R ) versus oval ( r) stamens, are linked and are 10 map units apart. You cross a homozygous blue-oval plant with a homozygous white-round plant.
Two Genes Crucial for Plants Colonizing the Earth 470 ... - SciTechDaily They specifically demonstrated that two genes are crucial for terrestrial plants to protect themselves against fungal attack - a defense mechanism that dates back 470 million years. These defenses most likely paved the way for all terrestrial plant life. Mads Eggert Nielsen, a University of Copenhagen biologist.
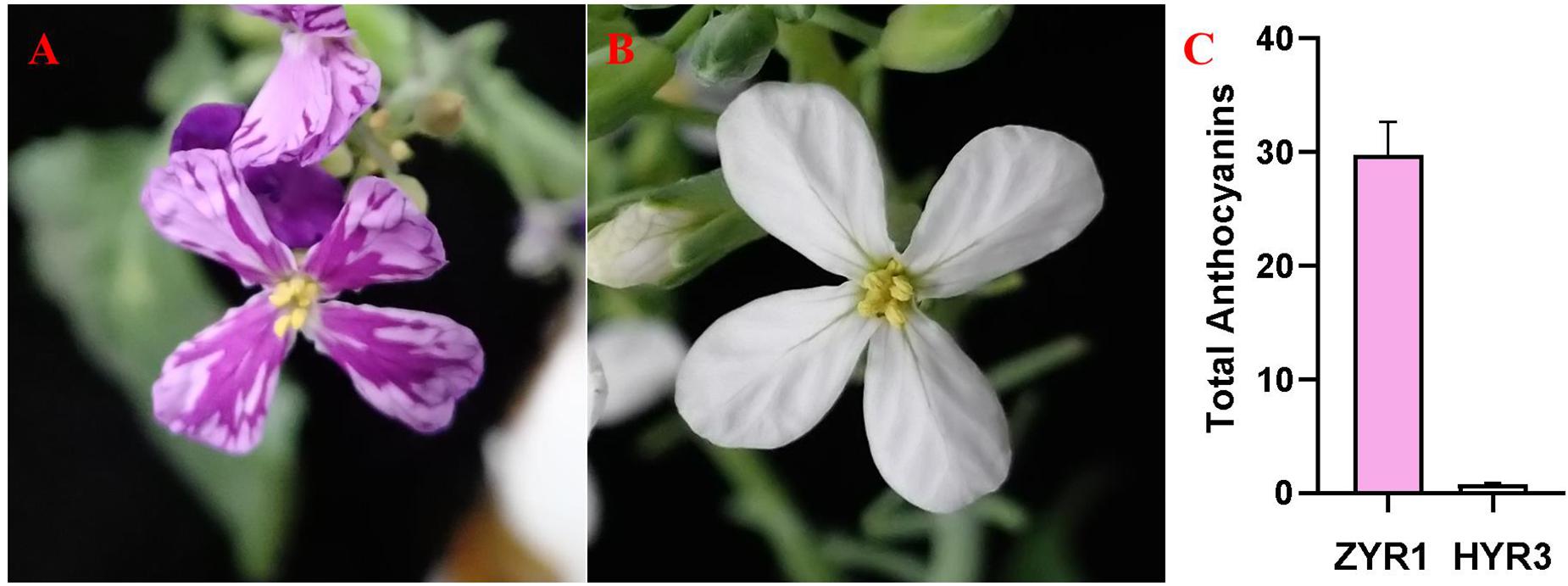




























Post a Comment for "43 two genes of a flower"