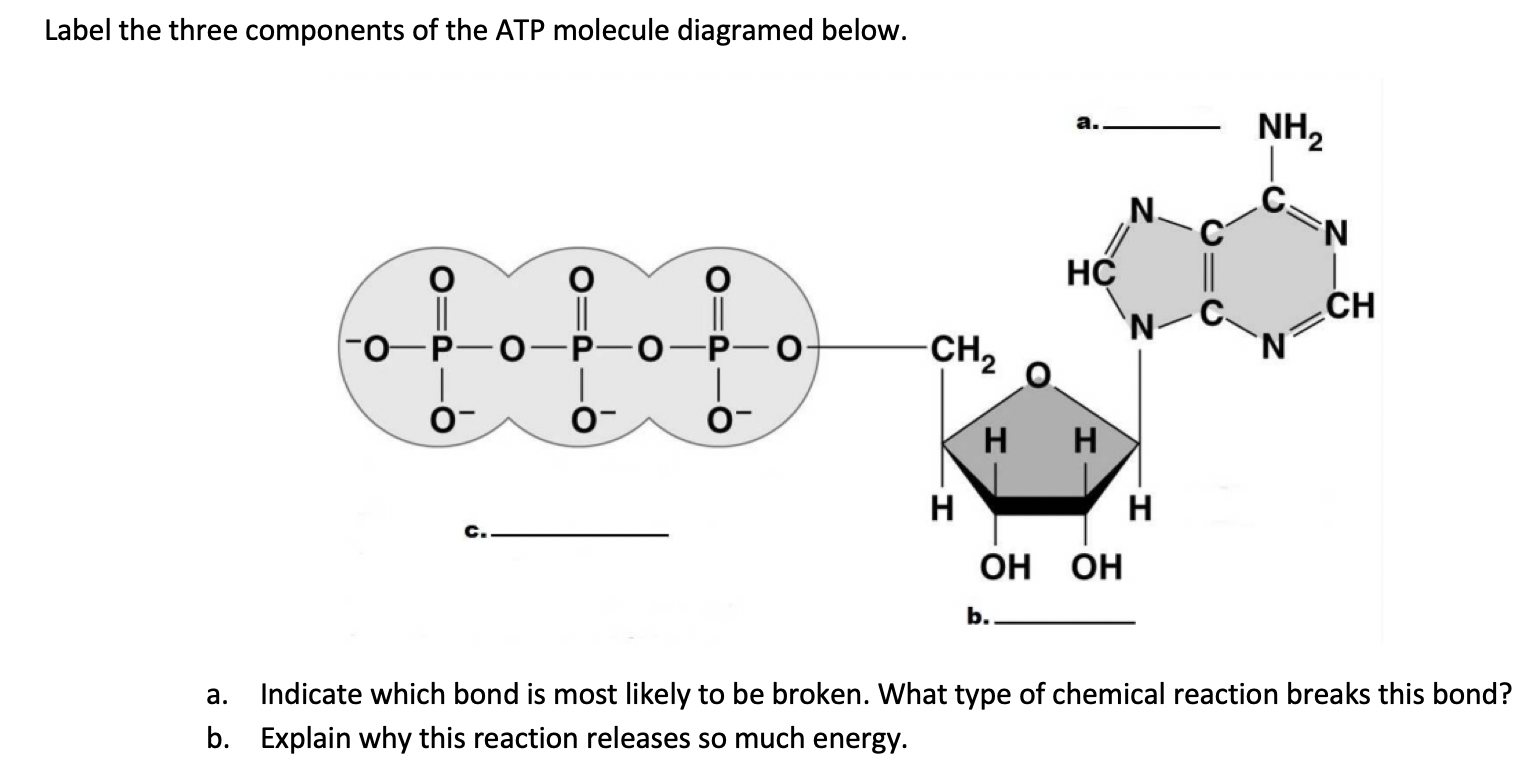
43 draw and label atp molecule
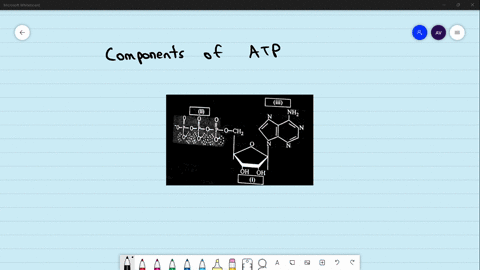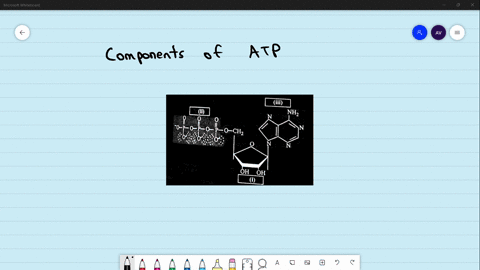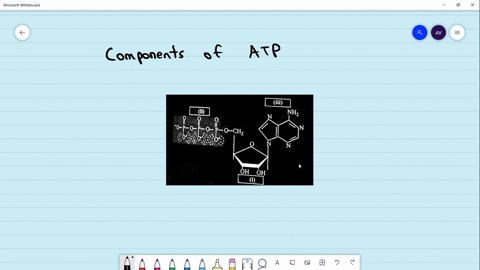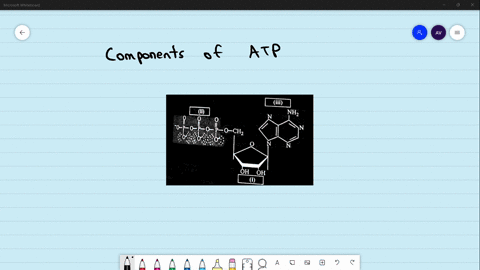
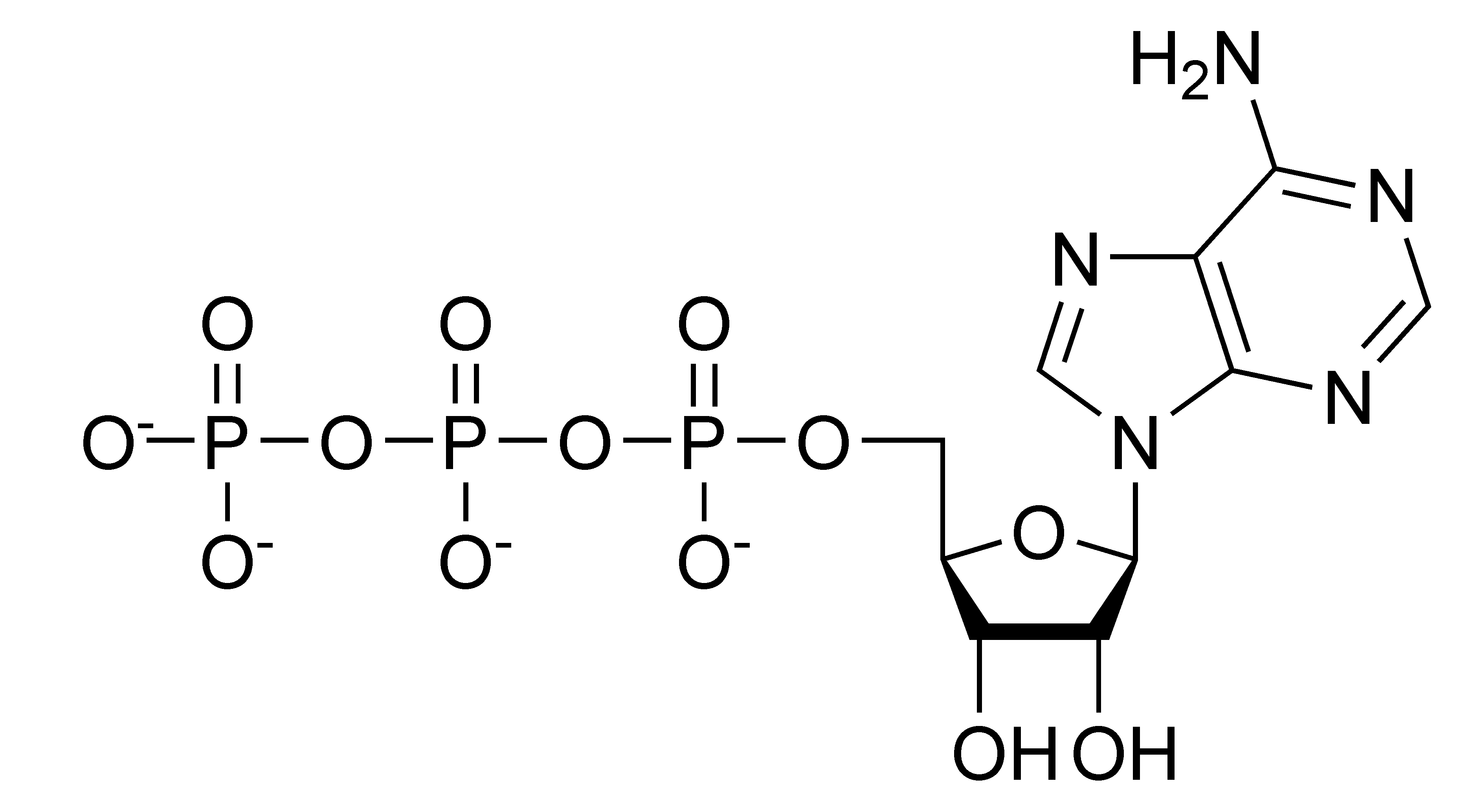
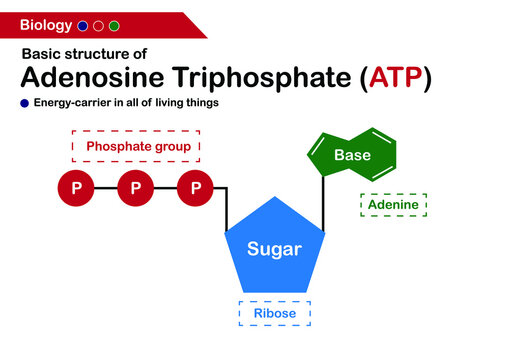
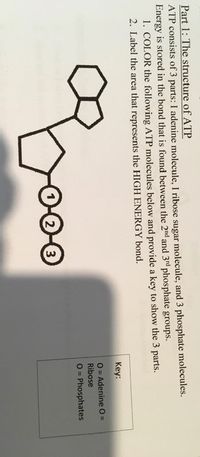
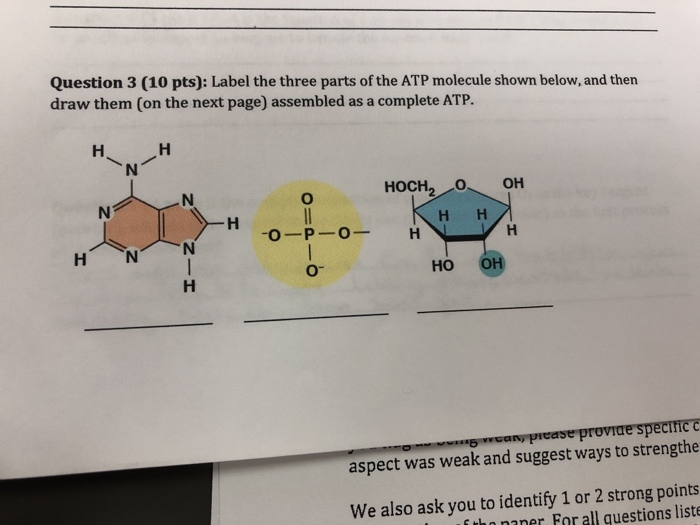
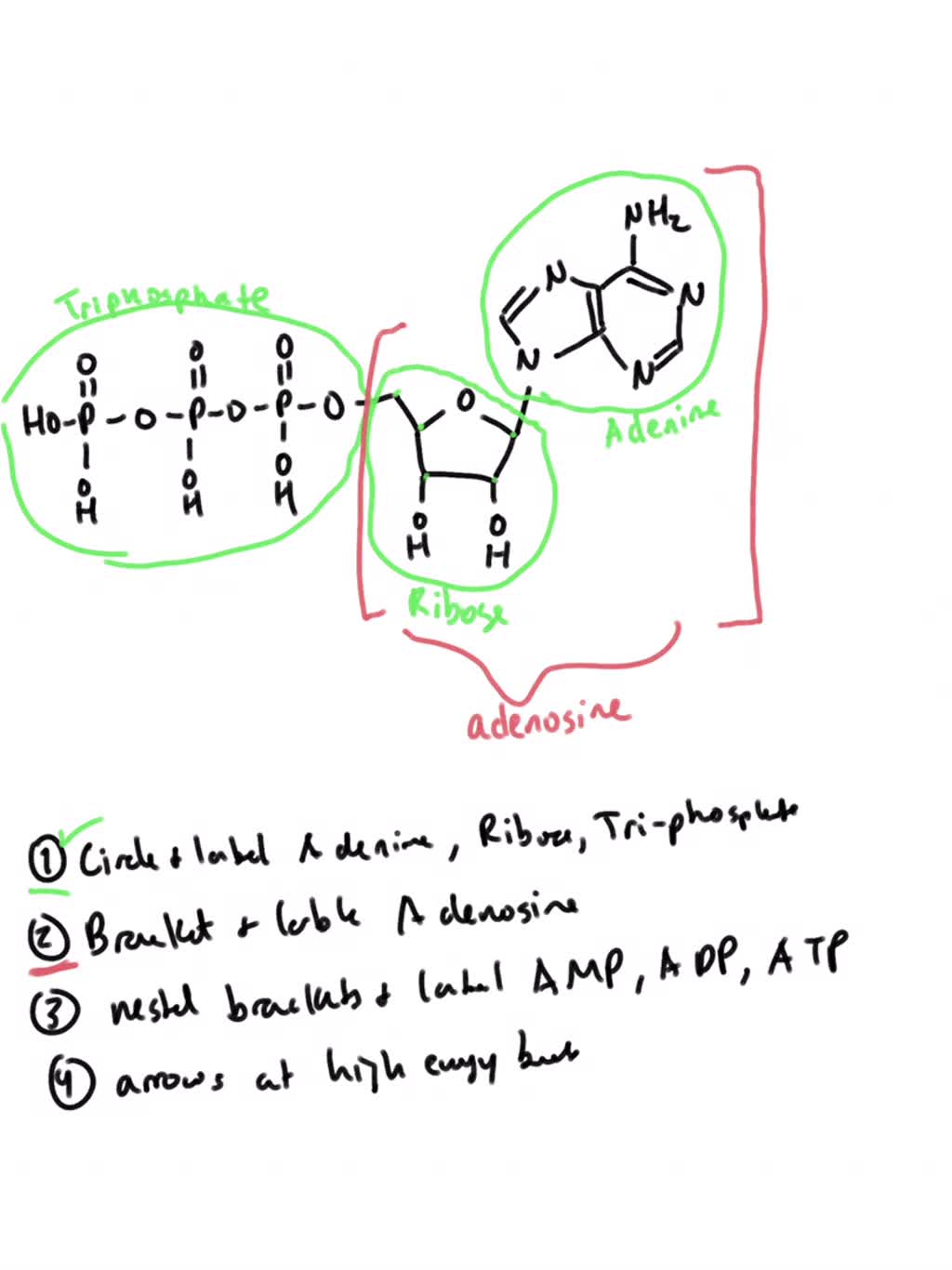
Structure of ATP - Learn Insta The Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecule is the nucleotide known in biochemistry as the "molecular currency" of intracellular energy transfer; that is, ATP is able to store and transport chemical energy within cells. ATP also plays an important role in the synthesis of nucleic acids. Solved 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and - Chegg 1) Draw a molecule of ATP, making sure to include and label the adenine, ribose, and three phosphates. 2) Discuss ATP's function as an energy molecule. Specifically discuss: how many phosphate groups would need to be removed from ATP to create the following molecules: Adenosine, AMP, and ADP.
ATP cycle and reaction coupling | Energy (article) | Khan Academy Adenosine triphosphate, or ATP, is a small, relatively simple molecule. It can be thought of as the main energy currency of cells, much as money is the main economic currency of human societies. The energy released by hydrolysis (breakdown) of ATP is used to power many energy-requiring cellular reactions. Image credit: OpenStax Biology.
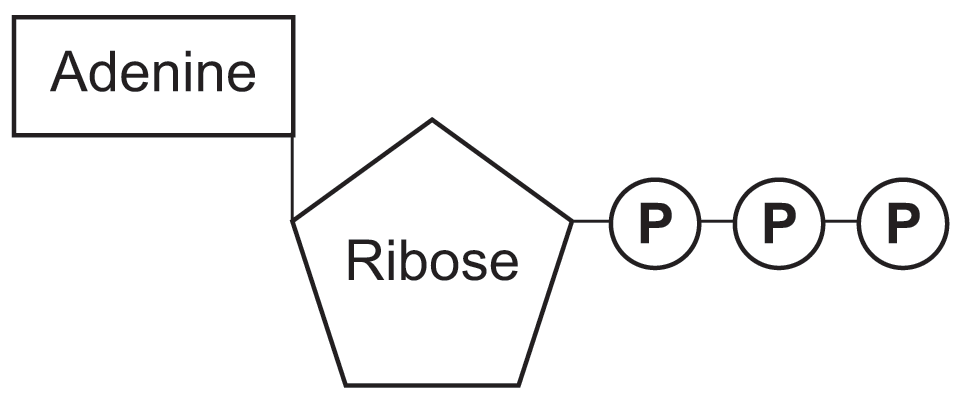
Draw and label atp molecule
BIO 201 Quiz 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label the regions of the mitochondria where the 3 different parts of cellular respiration occur How many ATP are generated from the glycolytic pathway? How many ATP are used to get the process up and running? What is the significance of this? What then is the main purpose of the glycolytic pathway in aerobic creatures? ATP: Definition, Structure & Function | StudySmarter ATP or adenosine triphosphate is the energy-carrying molecule essential for all living organisms. It is used to transfer the chemical energy necessary for cellular processes. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy for many processes in living cells. Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy NAD+ is an electron transport molecule inside the cristae of a cell's mitochondria. In glycolysis, the beginning process of all types of cellular respiration, two molecules of ATP are used to attach 2 phosphate groups to a glucose molecule, which is broken down into 2 separate 3-carbon PGAL molecules.
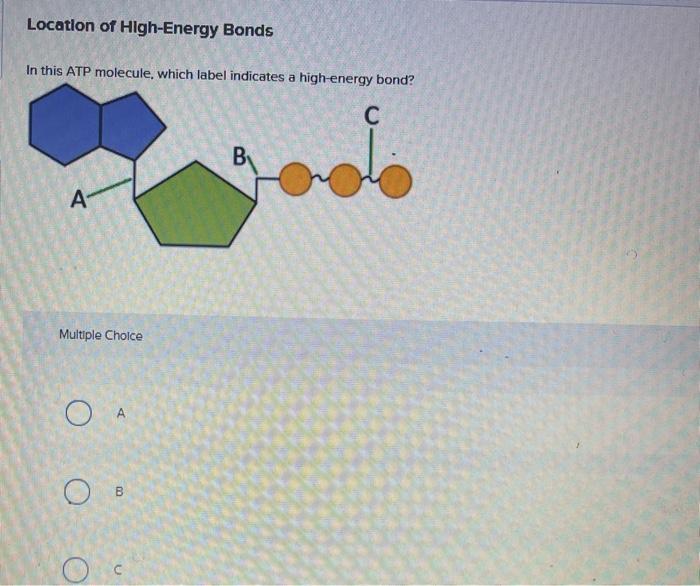
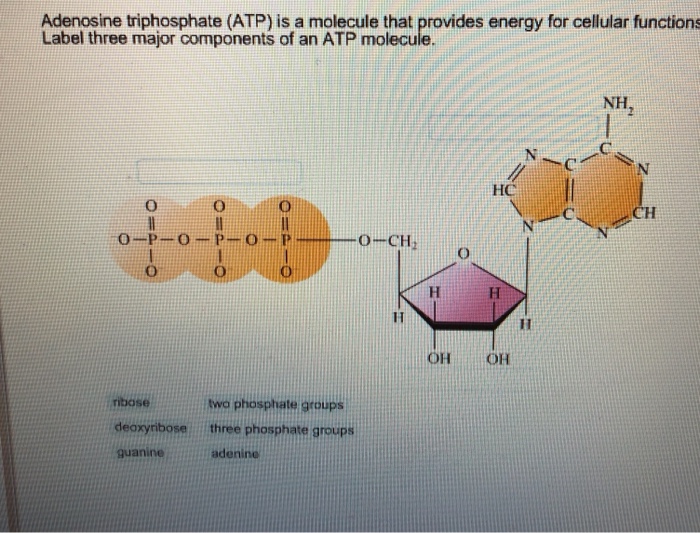
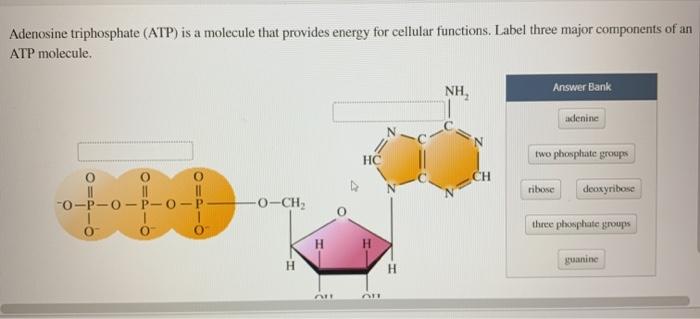
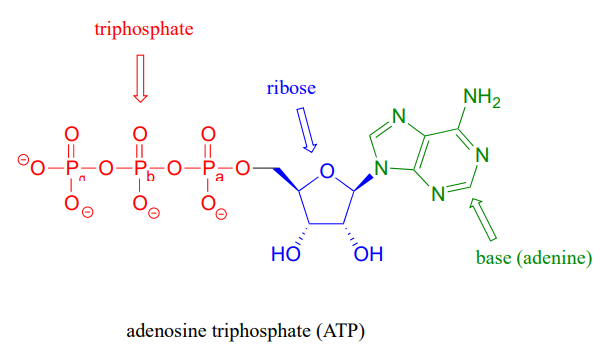
Draw and label atp molecule. Solved 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing - Chegg Question: 1. Draw and label an ATP molecule. Using your drawing as a diagram, explain how ATP molecules release energy. 2. How is ADP different from ATP? ADD has 2 phosphate ATP has 3 phosphate 3. Explain why glucose is important. groups groups 4. What is glucose broken down into during glycolysis? 5. Where does glycolysis occur? = 6. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) - Definition, Structure and Function Adenosine triphosphate, also known as ATP, is a molecule that carries energy within cells. It is the main energy currency of the cell, and it is an end product of the processes of photophosphorylation (adding a phosphate group to a molecule using energy from light), cellular respiration, and fermentation. All living things use ATP. Concept 2: Adenosine Triphosphate Flashcards | Quizlet The energy initially comes from carbon-based foods that we eat or even from sunlight. When a phosphate is removed, the energy that is released can be used for cellular work and chemical synthesis. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is considered by biologists to be the energy currency of life. label the parts of a molecule of ATP. (the ribosome) Label the parts of an ATP molecule? - Answers The three parts of an ATP, adenosine triphosphate, molecule are:A sugar (ribose)3 phosphates (the energy is stored in the unstable covalent phosphate bonds)Adenine (a double ring of carbon and...
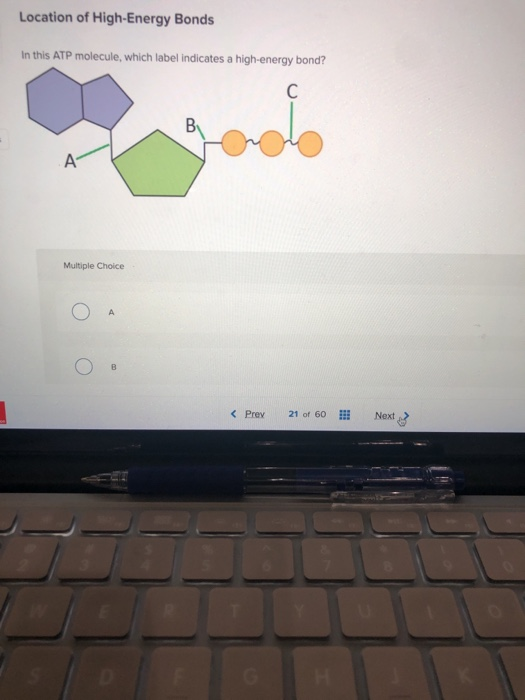
9.4: ATP, The Principal Phosphate Group Donor ATP is a versatile phosphate group donor: depending on the site of nucleophilic attack (at the α, β, or γ phosphorus), different phosphate transfer outcomes are possible. Below are the three most common patterns seen in the central metabolic pathways. A 'squigly' line in each figure indicates the P − O bond being broken. How do you draw a nucleotide and label its three basic parts? Explanation: The above structure is a nucleotide. It consists of a: phosphate group. 5-carbon sugar, and. nitrogenous base. What are three parts of an ATP molecule? | Socratic ATP molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions. Also notable, ATP stands for Adenosine Triphosphate. This molecule is composed of three parts: Adenine Ribose Three Phosphate Groups Here is a picture: Answer link Draw and label an ATP model please - Brainly.com Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP.
1. Draw and label the parts of an ATP and ADP molecule. . 2. Explain ... Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) consists of an adenosine molecule bonded to three phophate groups in a row. In a process called cellular respiration, chemical energy in food is converted into chemical energy that the cell can use, and stores it in molecules of ATP. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) | Definition, Structure, Function, & Facts adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Cells require chemical energy for three general types of tasks: to drive metabolic reactions that would not occur automatically; to transport needed substances across ... Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy NAD+ is an electron transport molecule inside the cristae of a cell's mitochondria. In glycolysis, the beginning process of all types of cellular respiration, two molecules of ATP are used to attach 2 phosphate groups to a glucose molecule, which is broken down into 2 separate 3-carbon PGAL molecules. ATP: Definition, Structure & Function | StudySmarter ATP or adenosine triphosphate is the energy-carrying molecule essential for all living organisms. It is used to transfer the chemical energy necessary for cellular processes. Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy for many processes in living cells.
BIO 201 Quiz 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Draw and label the regions of the mitochondria where the 3 different parts of cellular respiration occur How many ATP are generated from the glycolytic pathway? How many ATP are used to get the process up and running? What is the significance of this? What then is the main purpose of the glycolytic pathway in aerobic creatures?


























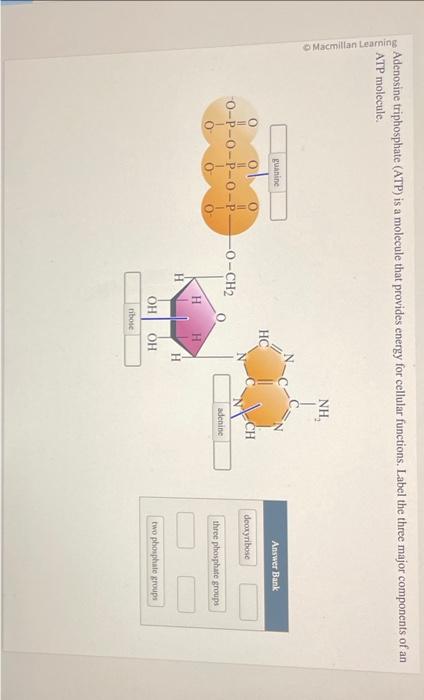

Post a Comment for "43 draw and label atp molecule"